The Role of Business Intelligence in Decision Making: Driving Success Through Data
In today’s increasingly complex and data-rich business environment, the ability to make well-informed decisions is critical for success. Business leaders must navigate an ever-growing stream of information to find meaningful insights that will help steer their organizations in the right direction. Business Intelligence (BI) has emerged as a vital tool to aid decision-makers by transforming raw data into actionable insights.
This article will explore the role of Business Intelligence in decision-making, its importance in various business functions, and how organizations can leverage it for strategic success.
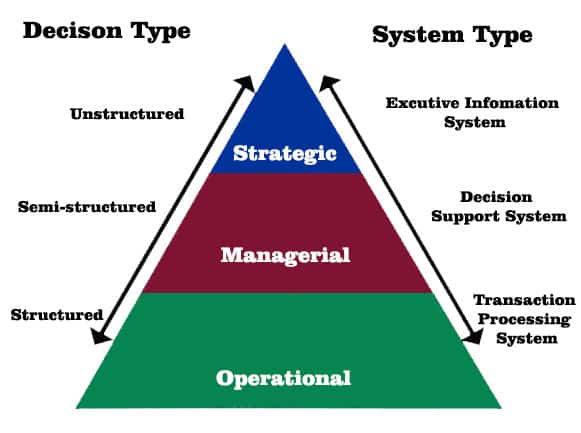
What is Business Intelligence?
Business Intelligence (BI) refers to the processes, technologies, and tools that organizations use to gather, store, and analyze data to support decision-making. BI transforms raw data from various sources—such as sales records, customer feedback, and operational reports—into useful insights. These insights enable businesses to identify patterns, trends, and anomalies, which helps them make informed decisions based on facts, rather than intuition or assumptions.
In simple terms, BI is a technology-driven process that helps businesses see the bigger picture and make better decisions using data analysis, reporting, and visualization tools.
The Importance of Business Intelligence in Decision Making
The role of Business Intelligence in decision-making has become essential in today’s fast-paced and competitive business landscape. Here’s why BI plays a critical role in helping organizations make better choices:
1. Data-Driven Decisions
One of the primary roles of BI is to empower decision-makers with accurate, real-time data. In contrast to traditional decision-making approaches that may rely on gut feelings or outdated information, BI allows businesses to make data-driven decisions.
For instance, instead of guessing which product to promote during a marketing campaign, a business can analyze sales data to determine the most popular items and tailor its strategy accordingly.
2. Improved Accuracy and Efficiency
Business decisions based on inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to costly mistakes. BI tools help ensure that data is clean, up-to-date, and easily accessible. They integrate information from various departments (such as finance, marketing, and operations), giving decision-makers a comprehensive view of the organization’s performance.
In addition to improving accuracy, BI can also enhance efficiency. Real-time reporting and dashboards reduce the time it takes to gather data, allowing for faster decision-making.
3. Identifying Opportunities and Threats
BI enables organizations to identify new opportunities and detect potential risks before they become significant issues. By analyzing trends, market changes, and customer behavior, BI helps businesses anticipate future developments. This foresight allows companies to be proactive, adjusting their strategies to capitalize on opportunities or mitigate threats.
For example, predictive analytics—a key feature of many modern BI platforms—can help companies forecast sales trends based on historical data, enabling them to prepare for seasonal fluctuations or new market demands.
4. Informed Strategic Planning
Strategic planning is essential for long-term success, and BI plays a significant role in shaping these plans. With BI, companies can track key performance indicators (KPIs), assess market trends, and measure the effectiveness of current strategies. This data-driven approach ensures that plans are based on factual information, helping businesses align their goals with real-world insights.
For instance, a retail company can use BI to analyze customer preferences and behavior, allowing them to develop a product launch strategy that resonates with their target audience.
5. Enhancing Competitive Advantage
In highly competitive industries, businesses that leverage BI for decision-making gain an edge over their competitors. BI helps organizations stay agile, allowing them to react quickly to changes in market conditions or customer needs. Companies that can access and analyze their data faster than competitors are more likely to spot emerging trends and adjust their strategies accordingly.
By continually monitoring competitor activities and market trends, businesses can stay ahead of the competition, identify gaps in the market, and innovate their offerings.
Key BI Functions in Decision-Making
BI is valuable in many areas of business decision-making, from day-to-day operations to high-level strategy. Here are several ways in which BI supports better decision-making across various business functions:
1. Financial Decision-Making
In finance, BI tools can help businesses track and analyze financial performance, monitor expenses, and forecast revenue. For example, a company’s finance department can use BI to compare revenue streams, manage cash flow, and identify cost-saving opportunities. Real-time financial reporting provides accurate insights into the organization’s financial health, ensuring that business leaders can make timely adjustments to their financial strategies.
BI also aids in risk management by identifying potential financial risks, such as unanticipated expenses or revenue shortfalls, allowing the business to address these issues before they escalate.
2. Marketing and Sales
BI plays a crucial role in marketing and sales decision-making by providing insights into customer behavior, market trends, and campaign performance. Marketing teams can use BI tools to track the success of their campaigns, analyze customer demographics, and evaluate product demand.
For instance, BI can help marketers identify which channels bring in the most qualified leads, allowing them to allocate their resources more effectively. Similarly, sales teams can use BI to monitor sales pipelines, predict closing probabilities, and optimize pricing strategies to increase revenue.
3. Operational Decision-Making
In operations, BI helps businesses optimize supply chains, improve inventory management, and streamline production processes. For example, manufacturers can use BI to analyze production data, identify inefficiencies, and reduce operational costs. By monitoring performance in real-time, businesses can quickly address bottlenecks or disruptions, ensuring smooth operations.
Additionally, BI can assist with resource allocation by identifying underperforming areas and reallocating resources to departments or projects that need them the most.
4. Human Resources
BI is also a valuable tool in human resources (HR) decision-making. By analyzing employee performance, retention rates, and hiring trends, HR departments can make data-driven decisions to improve workforce management.
For example, BI tools can track employee engagement metrics and identify patterns that lead to high turnover, allowing HR teams to address these issues proactively. BI also supports workforce planning by forecasting future hiring needs based on historical data and company growth projections.
How to Implement Business Intelligence for Decision Making
To successfully integrate BI into decision-making processes, businesses must follow a structured approach. Here are key steps for implementing BI effectively:
1. Identify Key Business Goals
Before implementing BI, it’s essential to identify the key business goals that you want to achieve. Whether it’s increasing sales, reducing costs, or improving customer satisfaction, having clear objectives will guide the BI strategy. This ensures that the data collected and analyzed is aligned with the organization’s priorities.
2. Select the Right BI Tools
Choosing the right BI tools is critical for success. There are various BI platforms available, each with unique features suited to different industries and needs. Some popular BI tools include Microsoft Power BI, Tableau, and QlikView. When selecting a tool, businesses should consider factors such as scalability, ease of use, and compatibility with existing systems.
3. Data Collection and Integration
The next step is to collect and integrate data from various sources within the organization. This can include sales data, customer information, operational metrics, and financial records. It’s important to ensure that the data is accurate and up-to-date to make informed decisions.
A data warehouse or cloud storage solution can be used to store and manage the data centrally, making it easily accessible for analysis.
4. Data Analysis and Visualization
Once the data is collected and integrated, BI tools can be used to analyze it and generate reports. These reports can be customized based on the business’s specific needs, providing decision-makers with insights relevant to their goals.
Data visualization is also a key feature of BI. Dashboards and interactive charts help simplify complex data, making it easier for stakeholders to understand and interpret the insights.
5. Training and Adoption
To ensure successful implementation, employees and decision-makers need to be trained on how to use BI tools effectively. Providing training sessions and encouraging a data-driven culture within the organization will help employees leverage BI for day-to-day decision-making.
Conclusion
Business Intelligence has become an indispensable tool for decision-making in today’s digital world. By providing organizations with access to accurate and timely data, BI enables businesses to make informed, data-driven decisions that improve performance, enhance efficiency, and boost competitiveness.
From financial forecasting to marketing optimization, BI plays a critical role in helping businesses identify opportunities, reduce risks, and make smarter, faster decisions. As the demand for data-driven insights continues to grow, companies that embrace Business Intelligence will be better positioned for long-term success.
In a world where decisions can make or break a company, BI offers the tools needed to make decisions with confidence and precision.